Corrective Osteotomy [Re-alignment]:
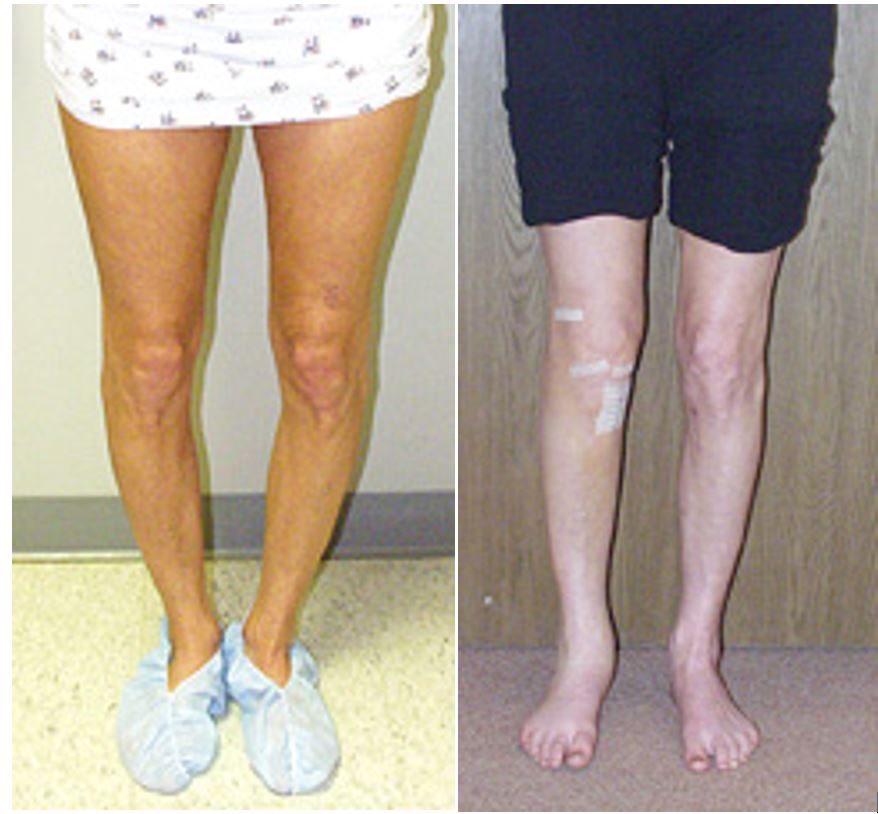
Corrective Osteotomy is an operation that realigns the lower leg to allow an even distribution of weight-bearing forces across the knee.
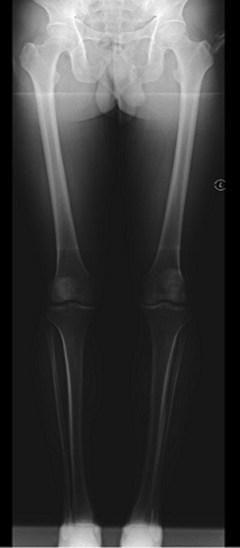
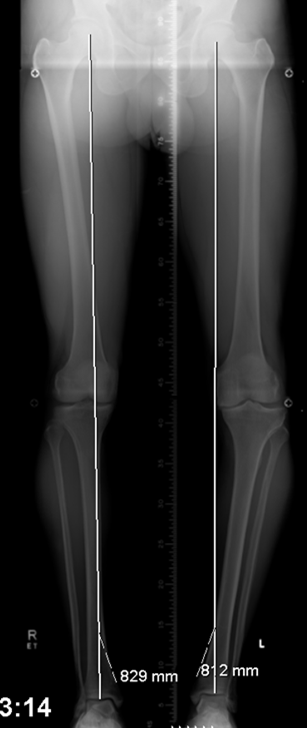
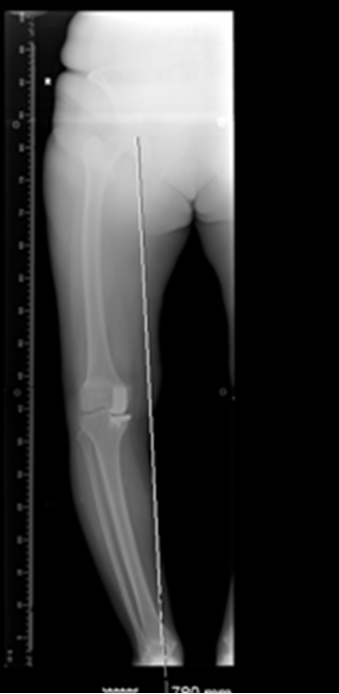
There are two types of alignment problems that can occur to the lower leg:
- valgus malalignment (or knock-knee)
- varus malalignment (or bowed knee): more common condition.
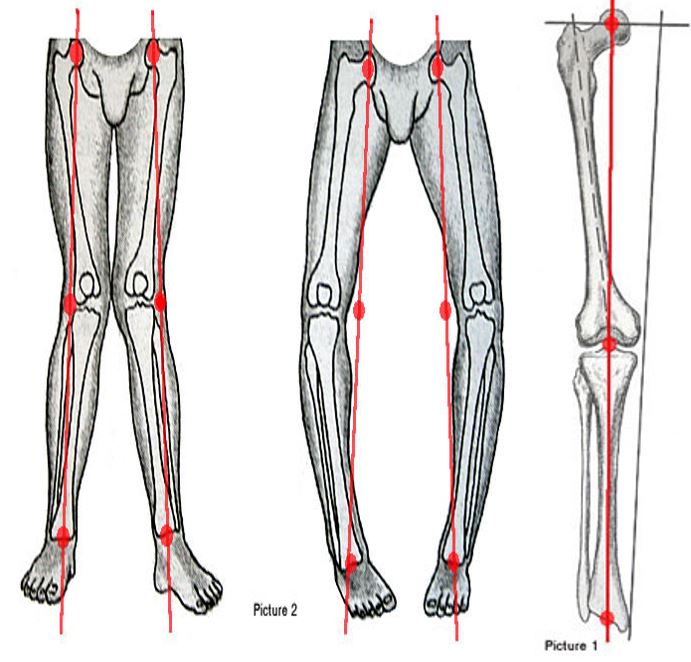
There are two types of Osteotomy, an opening wedge and a closing wedge.
Opening wedge:
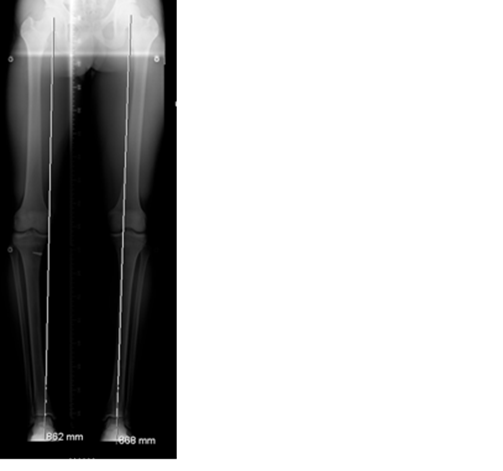
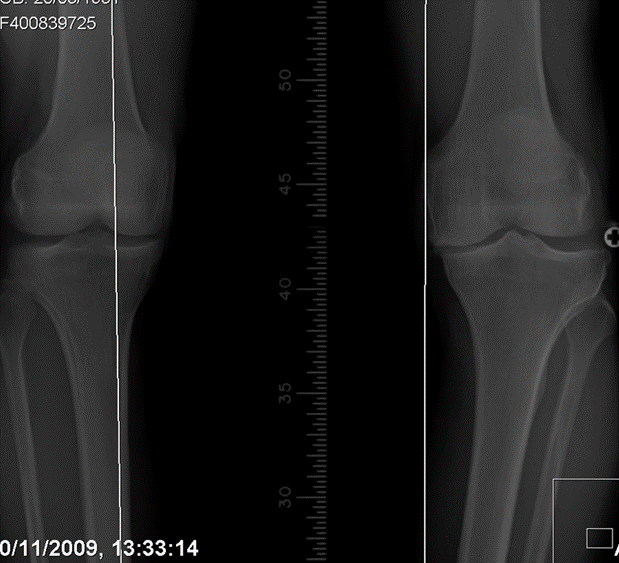
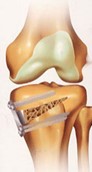
A small fracture is created in the upper portion of the tibia (shin bone). The fracture site is opened far enough so a space is created to then allow a small piece of bone to be inserted into this space.
Secure internal fixation is used to promote adequate healing.
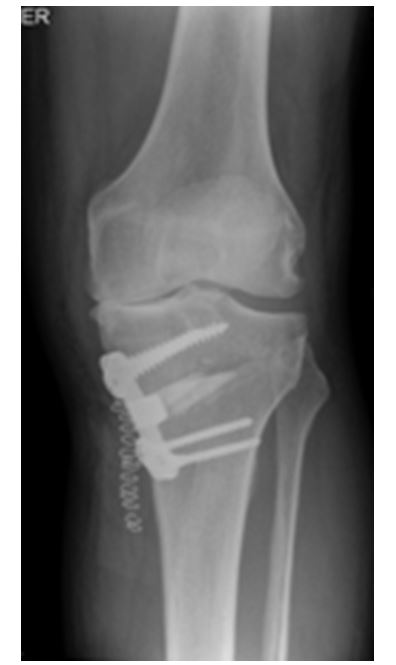
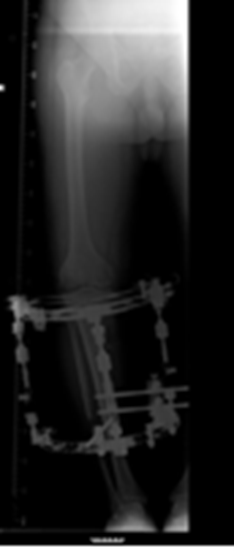
Closing wedge:
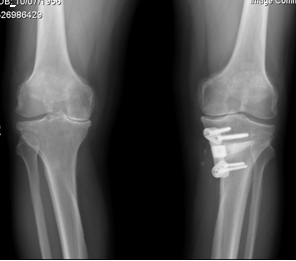
A small fracture is created in the upper portion of the tibia (shin bone) and sometimes in the fibula as well. A small wedge of bone is removed and the space is closed so that the ends of the fracture are together. Secure internal fixation is used as shown in the x-ray.
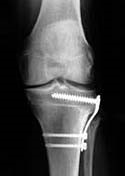
X-ray shows the internal fixation used in a closed Osteotomy.
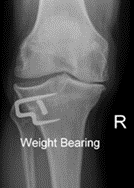
X-ray shows the internal fixation used in closed Osteotomy
The rehabilitation program after Osteotomy is:
- Knee motion and quadriceps strengthening exercises initiated the day after surgery
- Crutches for 6 weeks, with limited weight bearing in the initial weeks until the Osteotomy has progressed to an advanced healing stage.
- No sports until approximately 6 months postoperatively, and only for select patients who had limited or no damage to the joint lining. The majority of patients who have this operation are advised to return to light recreational activities only.
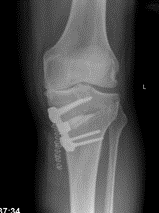
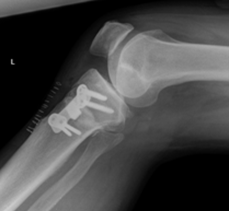
Open wedge tibial osteotomy
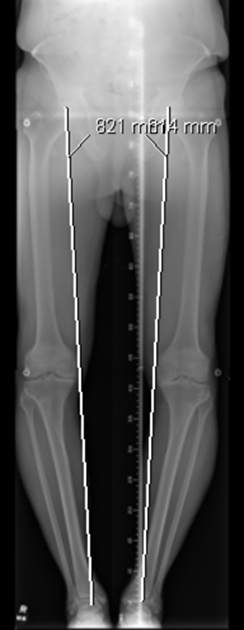
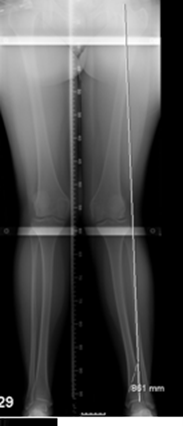
Long Mechanical axis film [Varus malalignment]